“For me, AGI is the equivalent of a median human that you could hire as a co-worker. It could do anything that you’d be happy with a remote coworker working behind a computer, which includes learning how to be a doctor or learning how to be a very competent coder.”
– Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI
What is AI and AGI? Many individuals are seeking information to tell the difference between the two, especially in the era when machine learning is advancing.
AI, also known as artificial narrow intelligence (ANI) or weak AI, is the broad field of computer science that uses pre-programmed rules & algorithms and supervised learning to perform tasks as per specific instructions within a defined context. Whereas artificial general intelligence (AGI) is a subset of AI (artificial intelligence) designed to emulate human cognitive abilities by leveraging unsupervised learning to solve problems on its own and adapt to a range of contexts.
In the debate between AGI vs AI, examples of AI include self-driving cars, predictive modeling, and factory AI. On the other hand, examples of AGI include generative AI, robotics, and advanced chatbots.
While predicting the future of AI, the concept of artificial super intelligence (ASI) is gaining popularity. It’s more like a theoretical and hypothetical concept of artificial intelligence aimed at manifesting cognitive skills and developing advanced thinking functions.
ASI is further evolving into large language models (LLMs), multisensory AI, and AI-generated programming to enable cross-domain learning and make connections between different fields.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
As discussed above, artificial intelligence is a wide-ranging branch of computer science that focuses on technologies that enable machines to perform advanced functions associated with human intelligence. These technologies are developed using machine learning and deep learning to facilitate AI applications like chess-playing computers, generative AI tools, and self-learning systems, amongst others.
The types of AI can be classified as ANI, AGI, and ASI. As you can see in the figure mentioned below, ANI caters to one specific area or context and problem solving within that area. Examples of AI in industry include virtual personal assistants, recommendation systems, fraud detection systems, and the like.
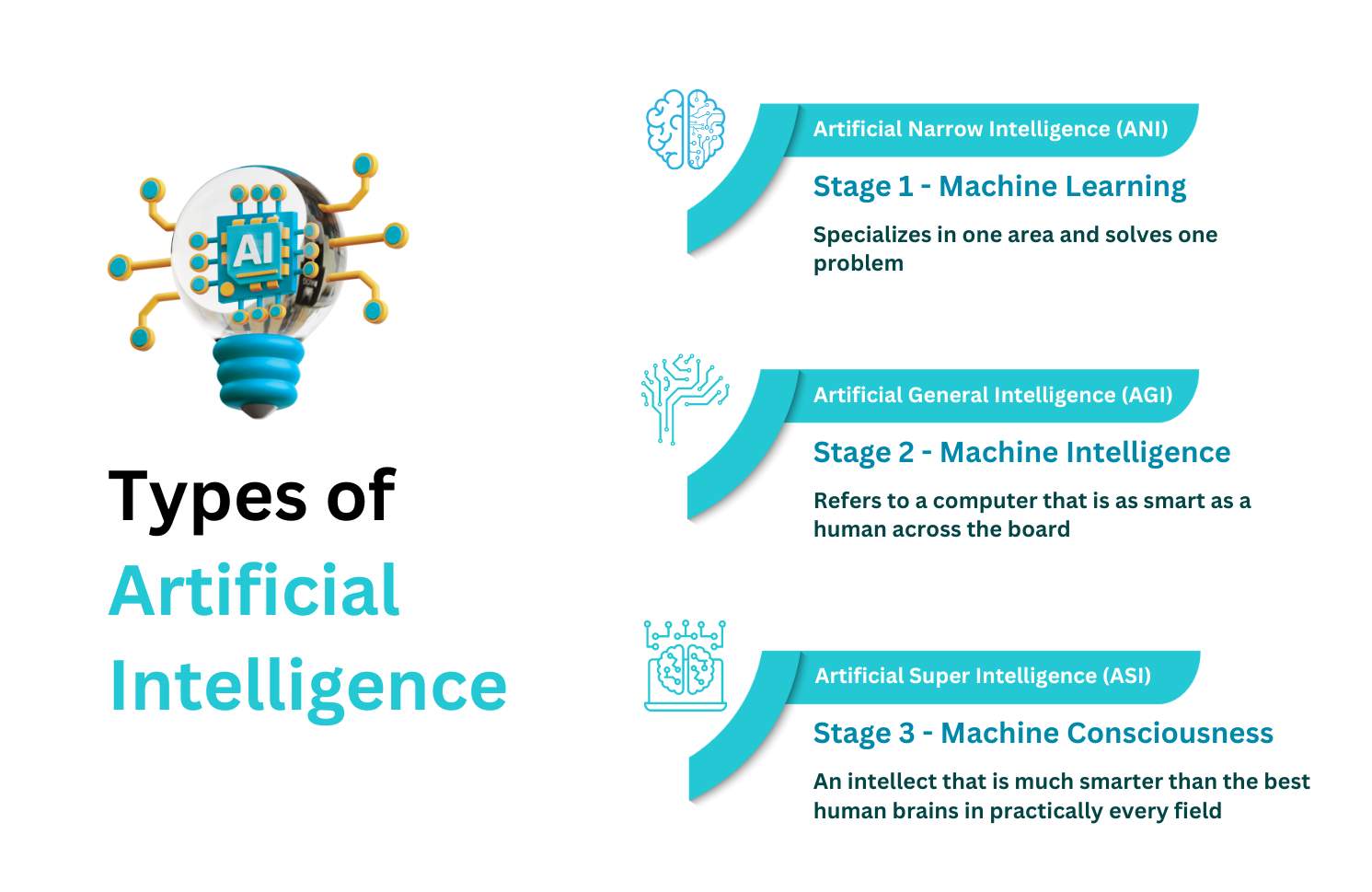
AGI on the other hand, also known as strong AI, is like the science-fiction version of AI, where its technology is integrated with human-level learning and can process information at unimaginable speeds. Since these machines are smart across the board, they are evolving to solve complex problems. For example, a self-driving car with built-in AGI can perform multiple tasks like picking up a passenger from a location, navigating roads, and answer questions the passenger asks about a location’s local culture.
Since ASI is still a theoretical concept, machines with ASI are capable of surpassing human intelligence to achieve tasks like low-to-no programming errors, increased success in defusing a bomb, and exploring potential oil mines.
What is Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)?
Just like ASI, even AGI is said to be a theoretical and hypothetical form of AI as developers are still working on improving machine intelligence that can complete new tasks for which it has never received training. Nonetheless, AGI is projected to gain prominence in industries like healthcare for analyzing massive amounts of data to identify patients at risk and in finance to execute informed trades based on real-time insights.
AGI is a field of theoretical AI research that can think, learn, and act the way humans do. Computer scientists and developers are collaborating to develop self-learning systems with problem-solving capabilities while adapting to their surroundings to complete various tasks.
For instance, companies like Amazon are hiring executives for their artificial general intelligence projects. They plan to partner with vendors specializing in enterprise AI tools to develop platforms that automate workflows.
Sessions at the AGI-24 conference in Seattle circled around AI agents capable of outperforming humans on tasks like playing digital games and diagnosing some forms of cancer.
China’s Taichi-II chiplet, predicted to power super-intelligent AI models, was unveiled in April 2024. This chip could power AGI systems to complete tasks like sorting different types of information and drastically improve the energy efficiency of electronic devices.
What is the Difference Between AI and AGI?
Before we dive deeper, let’s clarify what is AI and AGI. AI is a pre-programmed technology that can efficiently carry out a task, compared to a human. At the same time, AGI is the more ambitious machine technology with human-like intelligence that can deliver on tasks across a broad range of domains. To scale AGI to its full potential, advancing neural networks enables machines to adapt to new information and process complex patterns.
- Human-like Reasoning: AI or ANI excels within its specific domain owing to its predefined rules and patterns. However, it lacks the cognitive computing of the human mind. This is where AGI steps in to copy human-like reasoning for problem-solving and to manage a myriad of tasks.
- Scope of Tasks: AI refers to a machine that can mimic human intellectual capabilities. This includes delivering specific tasks like writing code, driving a car with driving-assistant features, or planning a birthday party.
AGI takes human cognitive abilities to the next level by learning, understanding, and applying knowledge into different fields. Unlike pre-programmed data in AI, AGI machines are untrained and non-programmed technology that can respond to complex queries, much like the recent LLMs such as GPT-4 and Google’s Gemini. - Understanding Context: AI systems like voice assistants might misinterpret a query if it struggles to grasp the context of the command. In such cases, AGI machines, if developed efficiently, can comprehend the context and facilitate decision-making during complex tasks.
- Learning and Adaptation: AI systems operate within the boundaries of their programming and are usually trained for tasks requiring large datasets. These intelligent systems reflect the human capacity to learn from one task and use that knowledge to execute new and unseen tasks.
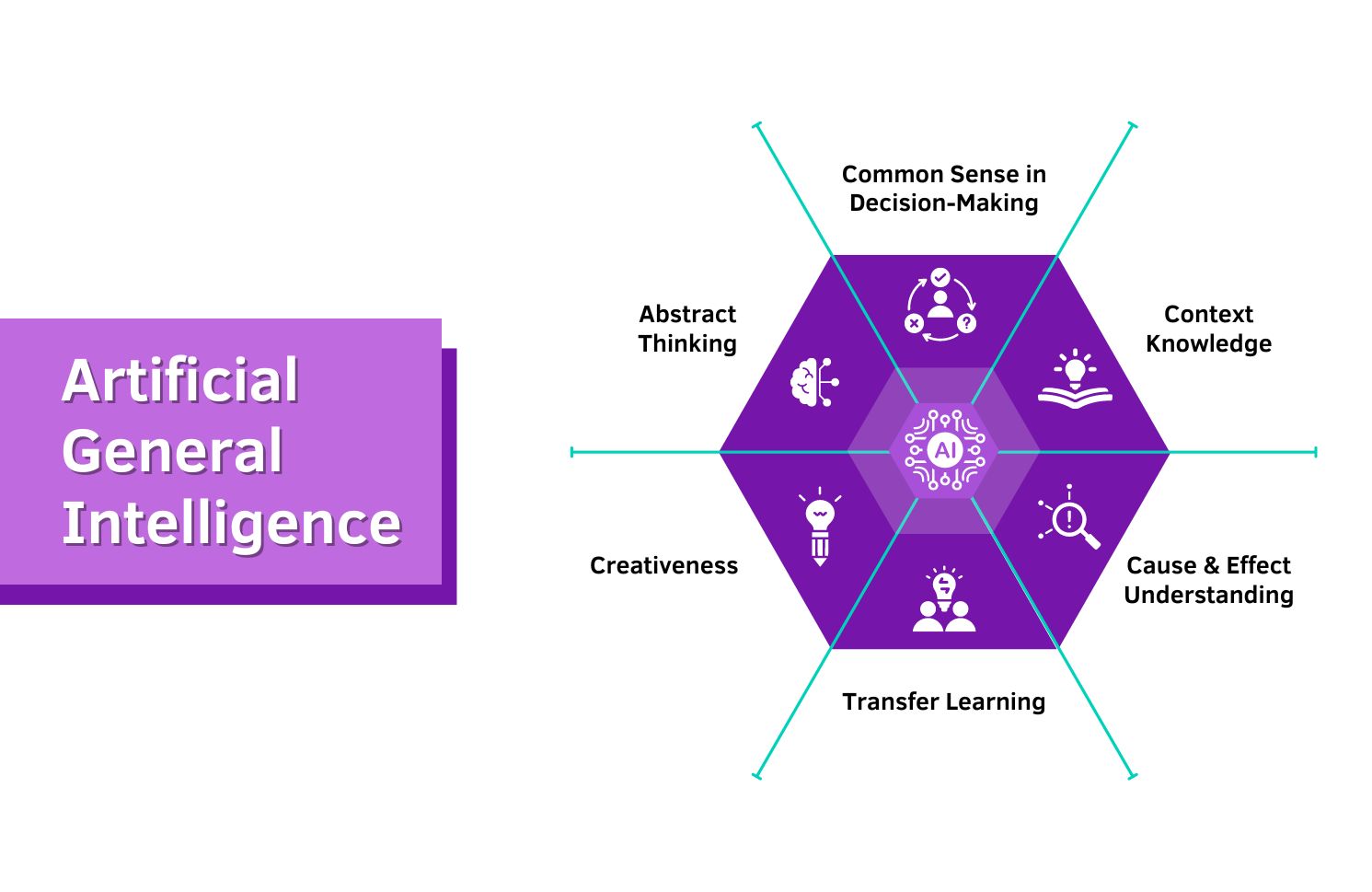
The above image illustrates the key functions of AGI, which, unlike specialized AI, is capable of learning and adapting to a wide range of tasks. This novel technology can predict and emulate human behavior to gain the ability to understand and reason across a myriad of scenarios.
While we continue to learn what is AI and AGI, AI is currently improving our lives but the emergence of AGI is a transformational leap in the technological universe, expanding the capabilities of machines to be more human.
Current State of AGI and AI Research Trends
The journey from narrow AI toward artificial general intelligence is challenging since it involves the efforts of researchers and developers to create machines that emulate human cognitive abilities. While we try to understand what is AI and AGI, let’s look at some AI limitations that developers are trying to overcome with research and technological advancements.
- Computing Power: Both artificial narrow intelligence and artificial general intelligence are power-hungry algorithms built on machine learning and deep learning. These systems require significant investment in core and GPUs (graphics processing units) to work efficiently. Nevertheless, researchers are developing chips that work efficiently in computers and improve performance for AI modeling and training.
- Common-Sense Reasoning: Human intellectual capabilities are based on a myriad of knowledge and the ability to overcome ambiguity. To ensure deep learning models perform human-level tasks, developers must create machines capable of processing large datasets, facilitating reinforcement learning, enabling hyperparameter optimization, and deploying unprecedented finetuning. However, common-sense reasoning is subjective in ML models, depending on domain-specific knowledge, individual experiences, and cultural contexts.
- Unreliable Results: As humans, we can deal with uncertainty. For instance, in situations where we lack information or deal with inconsistent insights, humans are able to navigate such situations using intuition, common sense, and probabilistic reasoning. Hence, researchers are required to conduct rigorous data analysis, facilitate continuous improvements in AI modeling, and constantly monitor the model’s results to adapt AI and AGI systems as per evolving situations.
- Self-Learning and Adaptation: Unlike artificial narrow intelligence which is based on predefined rules and patterns, artificial general intelligence thrives on autonomous learning and seeking information to expand its knowledge base. For instance, an AGI that plays board games should be able to apply the game’s reasoning and strategy skills to other complex scenarios that are beyond the scope of traditional AI.
- Problem-Solving: In traditional AI systems, there’s a need for better human-computer interaction to ensure the systems deliver the desired results. Meanwhile, emotional intelligence in AI systems is evolving to grasp the subtle nuances of real-world situations and generate novel solutions to complex challenges.
Ethical Considerations and Implications
It is important that artificial general intelligence and artificial intelligence systems operate safely and harmonize with human values. Here are a few AI ethics and safety considerations that are imperative as AI systems become more capable and autonomous.
- Intersection of Progress and Human Values: According to a research by Gartner, 50% of governments worldwide are predicted to implement responsible AI by 2026 through policies, regulations, and data privacy. Thus, with advancements in AI and AGI systems, it’s crucial to balance progress with subtle nuances of the human brain functions.
- Fair Distribution of AGI Benefits: Since AI and employment go hand-in-hand, AI technologists and end users need to expand moral philosophies to align with new working methods. Instead of increasing the risk of unemployment amongst labor-intensive industries like crane operations and car manufacturing, AI founders should offer training programs to operators instead of initiating mindless task automation. Though AI has benefits, it is unlikely to achieve zero bias in AI systems. Experts are researching ways to deploy AI technologies that do not lead to discriminatory harm.
- Responsibilities of Researchers and Businesses: Ethical AGI development requires governments, researchers, and businesses to prioritize interdisciplinary collaboration with experts. Stakeholders must gain a deep understanding of psychology, ethics, and sociology to comprehend the complex intersection of AGI and human values.
- Data Privacy and Security: Since ML models are trained using vast volumes of data and resources, chances are this data can be misused. This has created a demand for multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC) to secure AI models against unauthorized access. Apart from MFA and RBAC, data encryption, regular data audits, and data anonymization & pseudonymization play a vital role in the ethical collection, storage, and usage of personal data. In addition, AI governance helps to ensure that data privacy is protected.
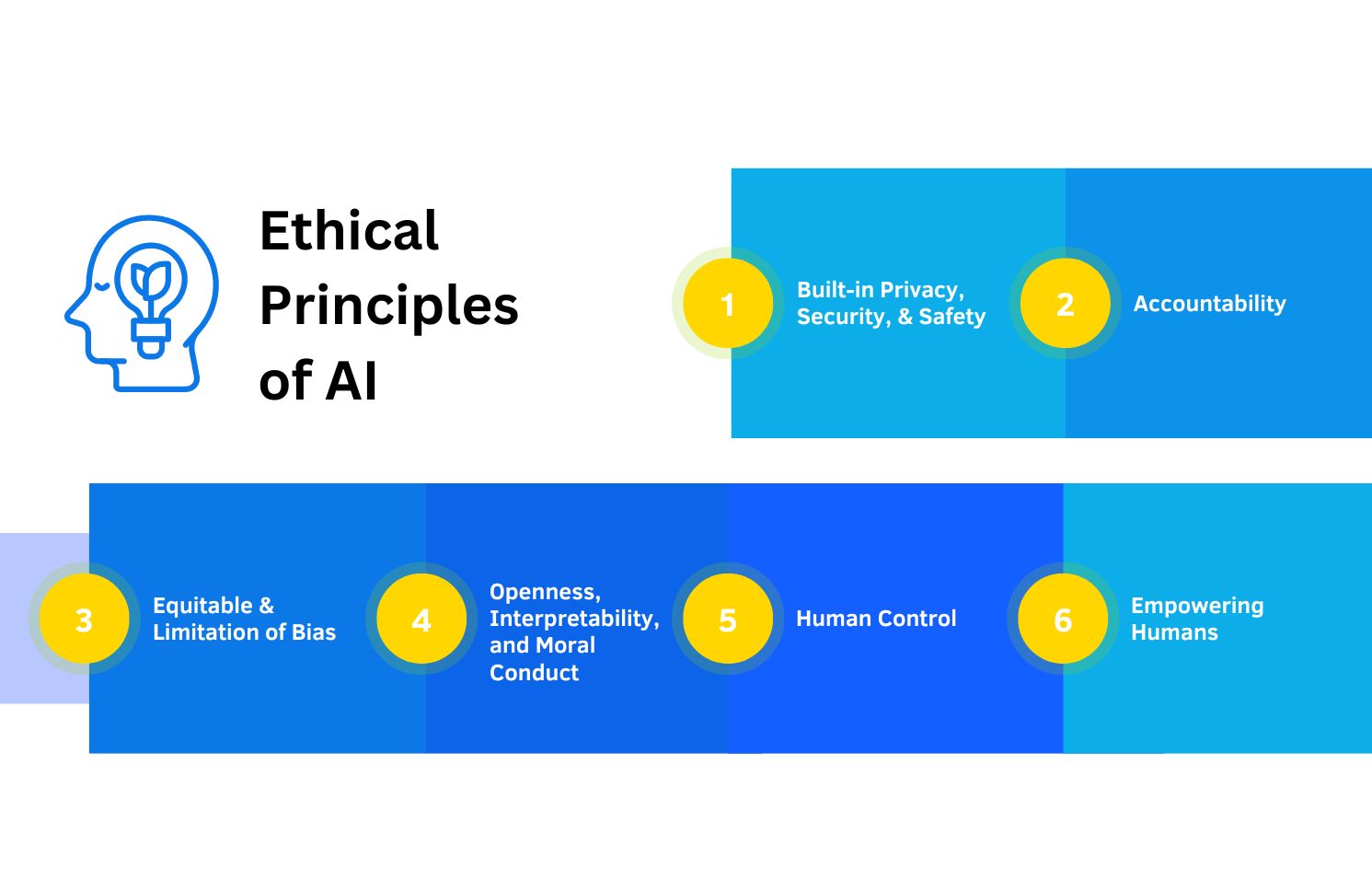
The above image demonstrates different ethical principles of artificial intelligence. An essential consideration in ethics principles are the development guidelines issued by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) to develop AI systems that are accountable, safe, and transparent.
Governments are predicted to fund research on the ethical development of AGI and promote its public education. The societal impact of AI is informing people about the potential impact of this game-changing technology. It is crucial for individuals to make informed decisions about the implementation of AGI and ensure AI safety.
The Future of AI and AGI
While researchers continue to explore what is AI and AGI, the progress in LLMs and AI technologies is striking an excitement for unprecedented possibilities with caution for risks. Let’s look at some future advancements in AI and AGI that could redefine the way we live and work:
- Ethical AGI: According to a Salesforce research, 80% of customers say knowing when they’re communicating with AI or a human is crucial. Hence, enterprises are ensuring accountability, safety, and transparency while communicating through chatbots and virtual assistants.
- Innovation and Discovery: AI is leading to trailblazing innovations in computer vision, engineering, medicine, and environmental science. This involves solving complex scientific problems, exploring new drug treatments, and optimizing renewable energy sources.
- Projects and Research: Advancements in natural language processing and data analysis represent a milestone in the history of AI. IBM Watson is one such breakthrough innovation that’s projected to assist in the treatment of diseases and offers data-driven insights to stakeholders from various industries.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Apart from predicting patient outcomes in healthcare, AGI can help businesses analyze market trends and provide operational data instrumental for strategic decision-making. In public policy, AGI is capable of modeling the impacts of various policy options.
- Learning in Real-Time: According to theories, artificial intelligence and AGI machines can emulate ambitious adults with a desire to expand their knowledge base. To achieve this, real-time learning will be a crucial feature in AGI, enabling systems to improve and refine data continuously.
- Personalized Education: Both artificial intelligence and artificial general intelligence are capable of creating tailored learning curricula for students. Natural language processing is expected to transform learning experiences with the potential to analyze words in a text to establish its general sentiment. This technology can help students improve their reading and writing by summarizing a text, paragraph, or document with a shorter text.
Make Your Business AI-Ready with Experts from AIT Global Inc.
Artificial general intelligence has the potential to handle complex tasks with emotional intelligence, creativity, and multi-dimensional thinking. To tap into the advantages of this novel technology, reach out to our team of AI engineers proficient in GenAI, data science & research, computer vision, and NLP.
Using our AI & ML services, organizations can devote their valuable time to analyzing market insights and using advanced statistical analytics to stay ahead of the competition. Before you leave, don’t forget to check our trending blogs on prompt engineering and generative AI that help clients with innovative approaches to deliver the finest quality solutions.






 What is XBRL: Learn the Definition, its Benefits, and Trends
What is XBRL: Learn the Definition, its Benefits, and Trends  Agentic AI vs Generative AI: What’s the Difference and Why It Matters
Agentic AI vs Generative AI: What’s the Difference and Why It Matters  The Hidden Costs of Incorrect EDGAR Filing and XBRL Tagging – And How to Avoid Them
The Hidden Costs of Incorrect EDGAR Filing and XBRL Tagging – And How to Avoid Them  What is Agentic AI and How It’s Transforming Business Operations
What is Agentic AI and How It’s Transforming Business Operations  AI Tools For Small Businesses
AI Tools For Small Businesses